Phishing attacks have grown by 29% in 2021 when compared to 2020 according to an analysis by Zscaler’s ThreatLabz research team.
The researchers analyzed data from over 200 billion daily transactions and 150 million daily blocked attacks, and released the findings in the 2022 ThreatLabz Phishing Report.
The report, which is available here for download after filling out a form, identifies key phishing trends and targets of 2021 and includes predictions for the years 2022 and 2023.
Phishing continues to be a major cyber threat
Phishing continues to be a dominant threat in the world, but it is evolving. The research team noticed a 29% increase of phishing attacks in 2021. It attributes the increase to several factors: from the low level barrier to running phishing campaigns to improved security systems that organizations and home users implement to protect against malware and other forms of malicious attacks.
Social engineering attacks are on the rise, as these are harder to detect and stop according to the researchers.
Another factor that plays a role in the rise of phishing attacks is automation and toolkits that attackers may use. Ready-made phishing kits do not require Deep technical know-how and include “everything
required to wage an effective low effort email or web-based phishing attack”.
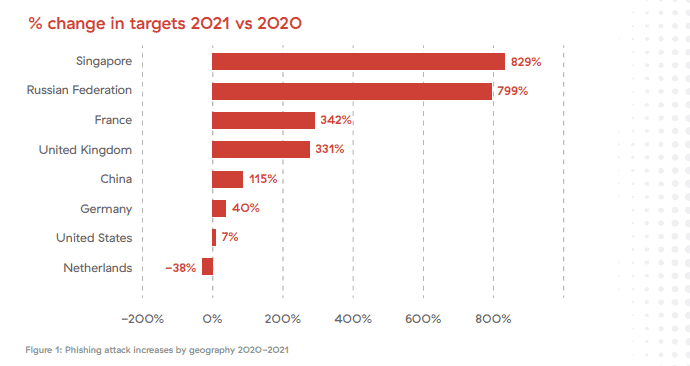
Phishing continues to be a global issue. While the United States continues to be the country that is targeted the most globally, with more than 60% of all blocked phishing attacks by Zscaler’s Security Cloud, it is not the only country that is suffering from these attacks. Placed next in the ranking are Singapore, Germany, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Russian Federation, France, China, Hungary and Ireland.
Zscaler’s system reported an increase in phishing attacks in 2021 for most countries in the top 10. Five countries saw an increase of over 100% each, with Singapore (829%) and Russian Federation (799%) leading the chart. Most, with the exception of Germany (40%), the United States (7%) and the Netherlands (-38%) saw large increases.
Phishing attacks target all industry sectors, but retail and wholesale, manufacturing, and services are targeted the most. Attacks on retail and wholesale targets saw an increase by 436% according to the report. Finance, government and all unspecified sectors saw increases by over 100% as well.
Attacks against these sectors capitalized on the worldwide pandemic and the consumer push to buying goods online.
Several industries saw a decline in phishing attacks in 2021. Zscaler’s research term lists technology and communication, services and healthcare as the three sectors with reduced attacks.
Microsoft, Illegal Streaming and Covid-19 most targeted
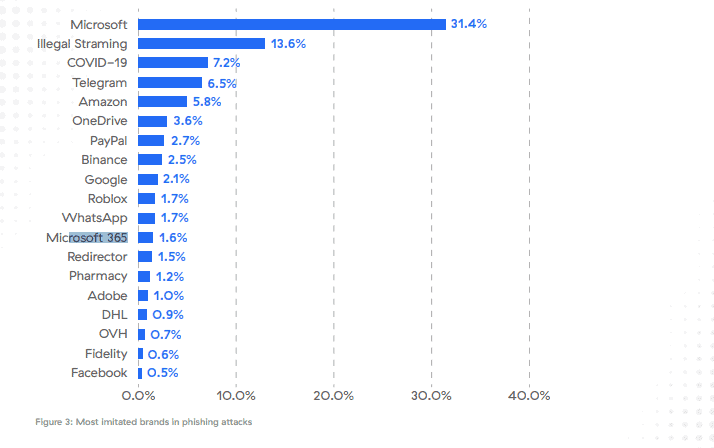
More than 30% of all phishing attacks imitated Microsoft in 2021, 13.6% imitated illegal streaming sites, and 7.2% imitated Covid-19 sites. Illegal streaming phishing spiked during large sporting events, including the Tokyo Olympics in 2021. Covid-19 phishing emerged in 2020, the year the Covid Pandemic started, and continued to be a major threat in 2021.
The researchers provide no explanation for Microsoft’s large percentage, but explain that Covid-19 and illegal streaming phishing attacks have “lower barriers” than phishing attacks that imitate established brands. Consumers have little or no expectation how Covid-19 or illegal streaming sites should look like or how they are accessed. The use of new domain names does not raise the same level of concern as the use of new domains for established brands.
Two additional Microsoft services are listed separately in the top 20 listing. Microsoft’s file synchronization and hosting service OneDrive is placed sixth with a total of 3.6%, and Microsoft 365 is placed twelfths with 1.6% of attacks. Microsoft products make up more than a third of all attacks according to the chart. Telegram, Amazon, PayPal, Binance and Google are also included in the listing.
Evolving Phishing trends
Zscaler’s research term saw increasing uses of safe domains and trusted platforms in phishing attacks. Threat actors use different methods to run their attacks. Advertising, the using of share sites like Evernote or Dropbox, and the posting of messages on forums, marketplaces or web blogs, are commonly used in attacks.
The list of top referring sites include google.com, adobe.com, evernote.com, luxherald.com, or googlesyndication.com.
Threat actors use different infrastructures to host phishing sites. More than 50% of all phishing sites use web hosting providers to blend in with legitimate sites, especially if IP addresses are shared between sites at the hoster.
Phishing as a Service got more traction in 2021. The use of phishing kits and open source tools has increased, and groups have been created that produce and update phishing toolkits. Attackers purchase toolkits to reduce costs and the time it takes to run phishing campaigns.
Besides requiring less technical knowledge to run, phishing toolkits include “sophisticated templates” that “have broadly eliminated the characteristic typos, spelling errors, bad grammar, and unsigned certificates previously relied on to identify phishing scams”.
Smishing, SMS Phishing, is another evolving trend. While it is been around since 2006 at the very least, smishing has seen a 700% increase in the first quarters of 2021 alone according to one report. One explanation for the increase in smishing attacks is that the attack type is not as widely known as email phishing. While computer users may be aware of email phishing, they may be less aware of other types of phishing, include SMS phishing. Another reason for the increase is, that it may be more difficult to verify the sender and loaded websites in mobile web browsers. Covic-19 scams and crypto-related phishing is also evolving.
Best practices to improve phishing defenses
Phishing attacks will continue to be a major threat in 2022 and beyond. The training of employees may reduce the likelihood of successful attacks against an organization’s infrastructure. A 2020 study by Stanford University reported that almost 88% of all data breaches were caused by human error. End user awareness training is critical, according to Zscaler’s report.
Organizations may implement technical defenses and policies to protect infrastructure and data against successful phishing attacks. Up to date antivirus software and advanced threat protection services, regular patching, email scanning, and encrypted traffic inspections are useful specifically.
The use of multi-factor authentication will stop most phishing attacks, as attackers can’t use a user’s username and password alone to sign-in to systems. The second layer of verification, which may be provided by an application or hardware gadget, blocks entry to systems. (via Born)
Thank you for being a Ghacks reader. The post Phishing Attacks grew by 29% in 2021 overall. Smishing is on the rise appeared first on gHacks Technology News.
