British researchers recently demonstrated that an algae-based energy collector, exploiting sunlight, could completely autonomously power a small computer for several months.
The power of algae
With the number of electronic devices constantly increasing, it is essential to find innovative ways to power them. Capable of producing hydrogen, forming the basis of biofuels, purifying wastewater, removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and generating electricity through photosynthesis, algae is a promising option, and it is on this last point that the team of thecambridge university concentrated.
Like natural solar cells, these tiny organisms convert sunlight into chemical energy, and water and carbon dioxide into organic molecules. A process produces electrons, which can be collected and used to power electronic devices.
Appearing to be no larger than an AA battery, their new device features a small container containing water and blue-green algae ( cyanobacteria of the kind Synechocystis). Electrons are collected by an aluminum electrode and sent to operate a ARM Cortex-M0+a low-power microprocessor commonly used in connected devices.
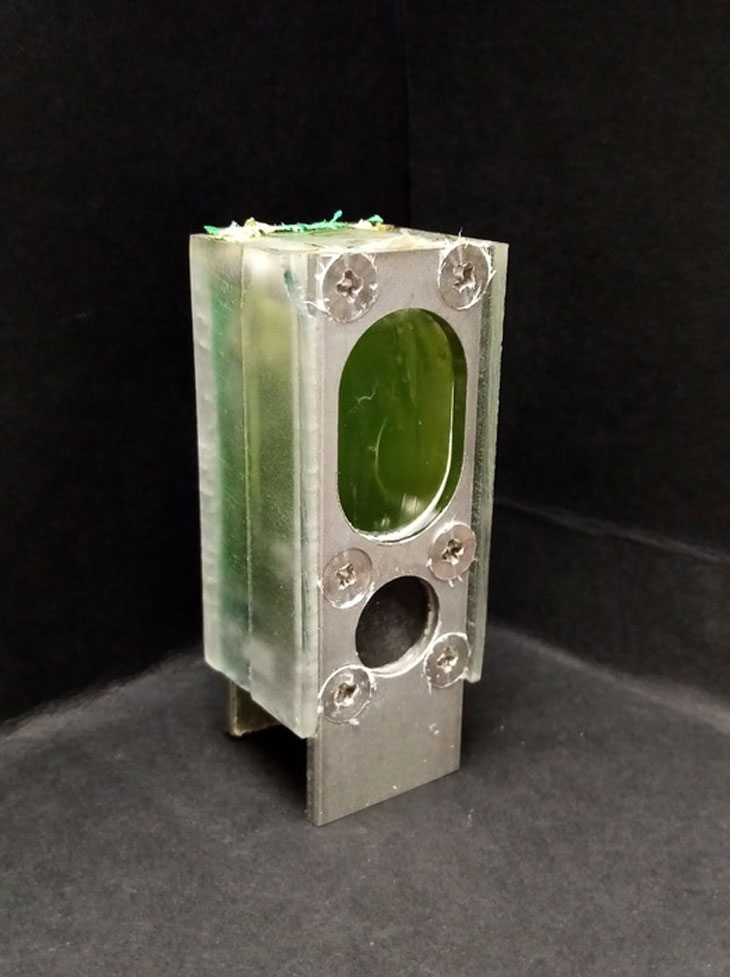
The researchers placed him in an environment domestic ” In the conditions ” semi-outdoor (near a window), where he was able to reliably and sustainably produce the electricity needed to operate the microprocessor. Although the article presenting it, recently published in the review Energy & Environmental Sciencefocuses on its first six months of operation, the team says such a device could operate for a full year.
A sustainable and more environmentally friendly source of energy
” We were impressed with the reliability of the system and its consistency over a long period of time. “, emphasizes Dr. Paul Bombelli, lead author of the study. ” We thought it would stop after a few weeks, but it kept working. »
The team says the device was even able to continue generating electricity in the dark, suggesting that blue-green algae may be storing some of their ” food and consume it later.
Manufactured from inexpensive and common components, and having a much longer lifespan than traditional lithium batteries, this type of collector/generator would be a much more environmentally friendly source of energy. According to the study authors, they could effectively power small electronic devices, especially in remote areas.
[related_posts_by_tax taxonomies=”post_tag”]
The post This algae-based generator powered a small computer for 6 months appeared first on Gamingsym.

