The development of science has allowed us to understand exactly how a living organism works, and what determines its functioning, why we look like our parents and what our features were originally laid down by nature. Many of the answers to these questions are in our DNA.
BY TOPIC: 1 barrel is how many liters?
What is DNA?
Behind this very abbreviation lies a name that is rather difficult to pronounce – Deoxyribonucleic acid.
The nuclein molecule was originally discovered by the Swiss biologist Friedrich Miescher in 1869. At first, it was considered a simple storage of phosphorus, there was no talk of any hereditary information in relation to the nucleic acid. Only in 1944, DNA was rediscovered to the world, already as the same carrier of hereditary information. Biologists have studied the transformation of bacteria and proved that deoxyribonucleic acid plays the main role in the process.
From the point of view of physics, DNA is a complex molecule that contains both hereditary information and is the actual instruction for the development of an organism from one universal cell. Many others, highly specialized for certain tasks, appear from it. In fact, DNA is not a molecule in the traditional sense. It is a double helix structure with chains linked by hydrogen bonds, which is much larger and more complex than a conventional molecule. Such chains are based on blocks of nucleides, which contain the very instructions for the development of the organism. DNA tells each cell which proteins to produce and how much.
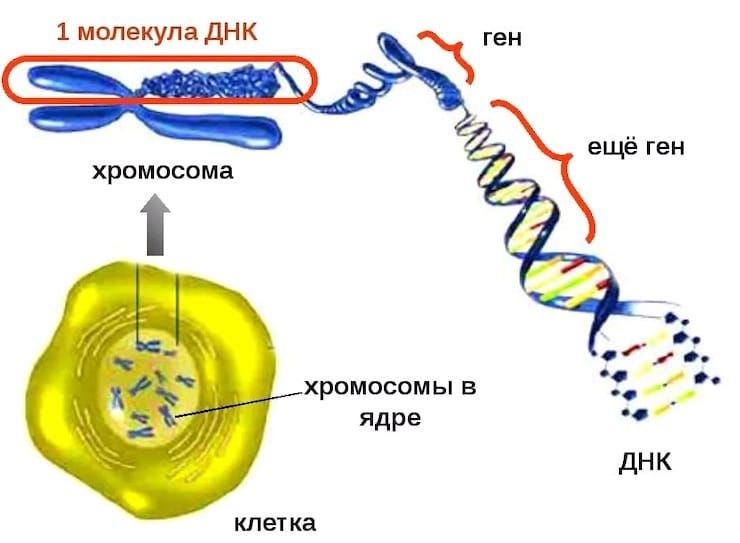
At the same time, in humans, 99.9% of the DNA is the same. All our differences are formed by only that tenth of a percent of our “biocode”. One can imagine the amount of information stored in DNA, given the diversity of people. Even a banana shares 50% of our DNA. And the scale of the molecule itself is impressive – if you unwind it, it will stretch for 2 meters. And in lilies and salamanders, the length of the molecules is ten times greater! But nature, using bending mechanisms, placed the DNA in the tiny nucleus of the cell.
BY TOPIC: What should be the pulse of a healthy person and how to measure it.
Are male and female DNA different?
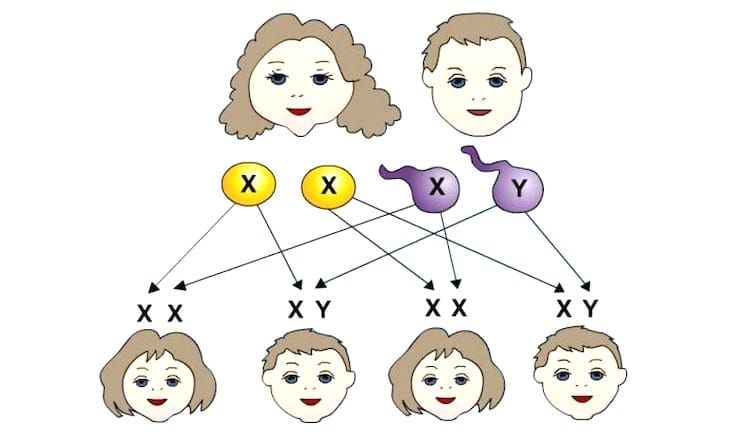
Most mammals have two sex chromosomes – females have two Xs, and males have an X and a Y. The division into two species occurred more than 100 million years ago. In the Y-chromosome, the SRY gene is significant, which triggers the male type of development of the organism. During fertilization, the egg combines with the sperm. From the mother, the child receives the female X chromosome (one of two identical), and from the father – either Y or X.
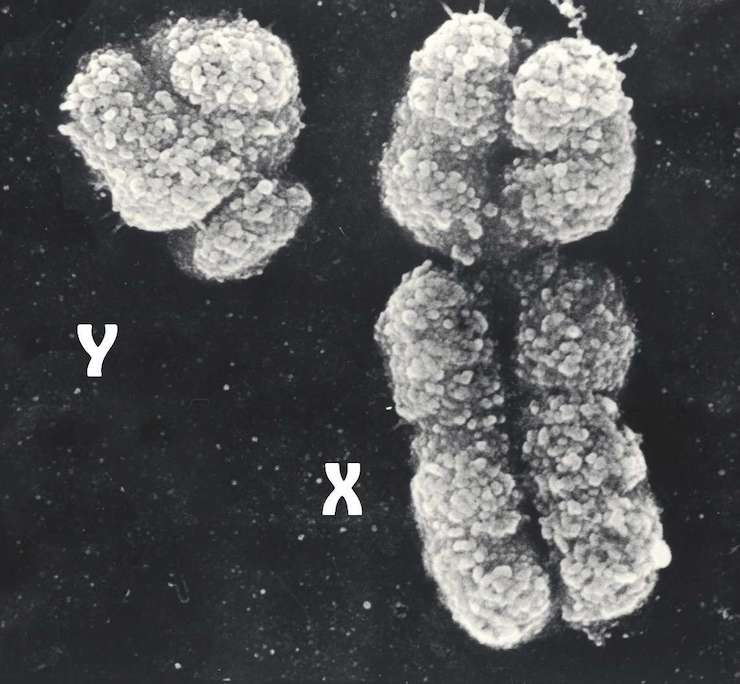
The final combination of XX means the birth of a girl, and the combination of XY will give birth to a boy. So don’t blame mothers for having babies of the “wrong” gender – father’s body plays a decisive role in this.
It is quite logical that new knowledge encourages them to use. If a person has discovered the very “brick” from which his body is built, then why not try to rebuild or even create something new? This will be the medicine of the future, but for now, knowledge about DNA allows us to solve smaller problems. One of them is DNA analysis, which allows deciphering some of its information. Back in 2003, scientists claimed to have located all the genes that determine our development and life.
BY TOPIC: Why don’t birds get electrocuted on wires.
How are genes different from DNA?
Genes and DNA are usually identified, but they are different concepts. Genes are formalized, with a beginning and an end, part of the chain. Proteins and RNA (ribonucleic acid), the single-stranded “mirror” of DNA, are encoded there. Within each gene there is a characteristic sequence of nucleotides. Genes encoding the structure and behavior of proteins occupy only 2% of all DNA. Another 1% of genes encode RNA. About 80% of all genes provide supportive functions, including compact DNA packaging. But scientists have not yet understood what the fifth part of DNA is responsible for.
BY TOPIC: How many calories do you need per day to lose weight for a man or woman, how to calculate.
How is a gene different from a genome?
The entire hereditary material of an organism, in which there are 3.1 billion base pairs, is called the genome.
The process of building new proteins from suitable 20 amino acids is carried out by the movement of the ribosome along the RNA. But the four nucleotides present in DNA are not enough for such coding. Nature has found a way out – it does not use the nucleotides themselves, but their sequences of three elements – the genetic code. This approach allows you to program as many as 64 amino acids. And although nature does not need so much, scientists have already thought about the potential of amino acids.
BY TOPIC: What is a placebo, how does it work, and is there really an effect?
What is needed for DNA analysis?

DNA analysis has become popular not only in medicine, but also in forensics, making it possible to prove the involvement of a suspect in a crime. Today, such a study is increasingly mentioned on scandalous talk shows where paternity is clarified. Comparison of the DNA of a child and his potential parent almost 100% gives an answer about a possible relationship. At the same time, complex biomaterial sampling is not required for analysis. DNA is contained in almost all living cells: in saliva, blood, semen, epithelium, earwax. But in order to get a reliable result, it is better to take blood from a vein for analysis directly in the laboratory. The analysis itself is carried out in several stages and requires the use of technological equipment and special reagents. That is why the DNA test is carried out in large clinics in large cities, but the sampling of biomaterial (a piece of a nail, a cotton swab in a test tube, traces of saliva) can be done on the spot, and then sent by mail. And although such a test will not have legal force, the result will be quite accurate.
In the course of reading a molecule, it is first isolated, then repeatedly copied and cut into pieces for analysis. Nitrogenous bases are stained with a special luminous dye, which is recognized by laser transillumination. Several DNA analysis methods have already been developed, they are constantly being improved by modernizing instruments and improving computer programs. This allows you to gradually reduce the cost of such analysis.
Our DNA is a real storehouse of information and, perhaps, the same magic wand that will allow us in the future to at least fight hereditary diseases and, as a maximum, modernize our bodies. And if immortality is a controversial issue that nature opposes, then the study of DNA can help in extending our life and improving its quality.
See also:
.
The post What is DNA: a simple explanation appeared first on Gamingsym.
