Microsoft’s Windows operating system supports several multicast name resolution protocols, including NetBIOS and LLMNR. The state of the art protocol that is widely used today is mDNS, while the protocols NetBIOS and LLMNR are not widely used anymore.
In Aligning on mDNS: ramping down NetBIOS name resolution and LLMNR, Microsoft informs Windows system administrators that it plans to disable the old protocols in future versions of Windows to improve device security and decrease the load on the networks they use.
Microsoft is aware that there are still scenarios and “real-world deployments” in which these protocols are used, but the company is convinced that disabling the protocols by default is the right direction to take.
The company has not started the process of disabling LLMNR by default yet, but it has started the process for NetBIOS.
The NetBIOS protocol is already turned off by default on cellular devices according to Microsoft. In the latest Windows Developer and Beta Insider builds, NetBIOS is in learning mode. Learning mode means that NetBIOS is used as a fallback if mDNS and LLMNR queries fail.
The change may lead to connectivity issues in some cases. Administrators may modify a Group Policy or a Registry value to change the behavior of the protocol.
Note: the Group Policy Editor is only available on Professional and Enterprise editions of Windows. Home edition administrators may modify the behavior in the Registry.
Changing NetBIOS in the Group Policy Editor
- Use the keyboard shortcut Windows-R to open the Run box on the system.
- Type gpedit.msc and hit Enter; this should load the Group Policy Editor.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > DNS Client.
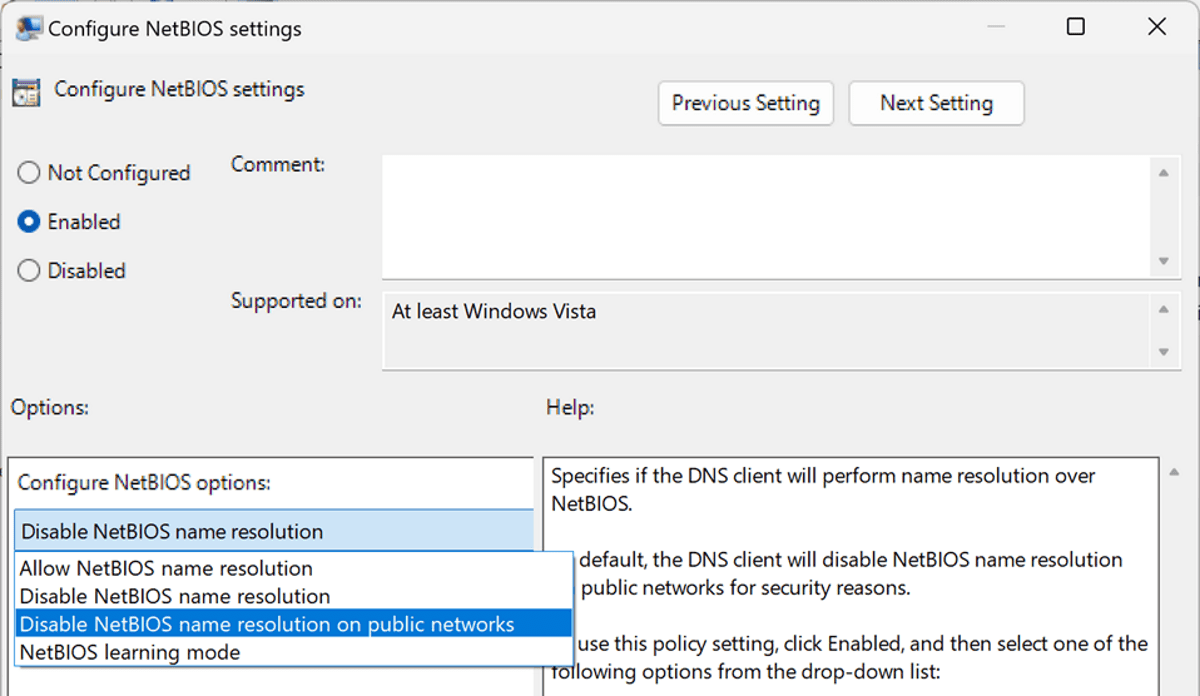
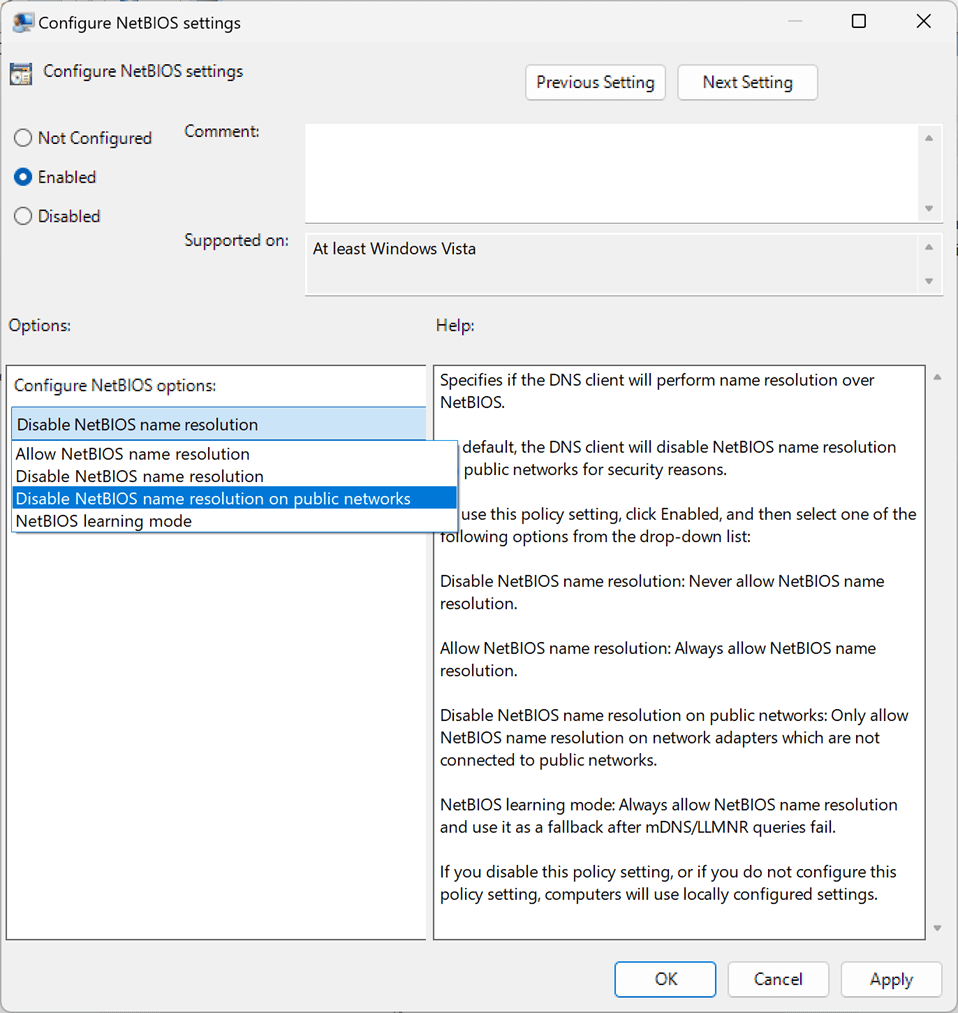
- Double-click on the Configure NetBIOS policy.
- Set the policy to Enabled.
- Use the menu that is provided “Configure NetBIOS options” to switch to one of the supported options:
- Allow NetBIOS name resolution — Enables full NetBIOS support.
- Disable NetBIOS name resolution — Turns off NetBIOS support on the device.
- Disable NetBIOS name resolution on public networks — Keeps NetBIOS enabled on private networks, but disables it on public networks.
- NetBIOS learning mode — NetBIOS is only used as a fallback if mDNS and LLMNR queries fail.
- Select OK to save the new policy setting.
Changing NetBIOS in the Windows Registry
The same options are also available in the Windows Registry.
- Use the keyboard shortcut Windows-R to open the run box.
- Type regedit.exe and hit the Enter-key.
- Navigate to Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Dnscache\Parameters in the Registry Editor.
- Right-click on Parameters and select New > Dword (32-bit) Value.
- Name the value EnableNetbios.
- Double-click on the new Dword and set it to one of the following values:
- 0 — Disabled.
- 1 — Allowed.
- 2 — Disabled on public networks.
- 3 — Learning Mode.
- Close the Registry Editor after you have made the change.
Closing Words
LLMNR has not been touched yet, but Microsoft plans to make similar changes to this protocol in future builds and versions of the Windows operating system.
Now You: do you use NetBIOS or LLMNR? (via Deskmodder)
Thank you for being a Ghacks reader. The post Microsoft starts to phase out NetBIOS and LLMNR to focus on mDNS appeared first on gHacks Technology News.
